 . The Chi-Rho symbol was also used by pagan Greek scribes to
mark, in the margin, a particularly valuable or relevant passage; the
combined
letters Chi and Rho standing for chrēston, meaning "good."
. The Chi-Rho symbol was also used by pagan Greek scribes to
mark, in the margin, a particularly valuable or relevant passage; the
combined
letters Chi and Rho standing for chrēston, meaning "good."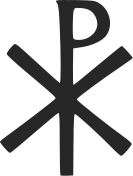
The Chi Rho is one of the earliest
christograms used by Christians. It is formed by superimposing the
first two letters in the Greek spelling of the word
Christ
(
Greek : "Χριστός" ), chi = ch and rho = r, in such a way to produce
the
monogram  . The Chi-Rho symbol was also used by pagan Greek scribes to
mark, in the margin, a particularly valuable or relevant passage; the
combined
letters Chi and Rho standing for chrēston, meaning "good."
. The Chi-Rho symbol was also used by pagan Greek scribes to
mark, in the margin, a particularly valuable or relevant passage; the
combined
letters Chi and Rho standing for chrēston, meaning "good."
Although not technically a cross, the Chi Rho invokes the crucifixion of Jesus as well as symbolizing his status as the Christ. There is early evidence of the Chi Rho symbol on Christian Rings of the third century.
The labarum (Greek: λάβαρον) was a vexillum (military standard) that displayed the "Chi-Rho" symbol, formed from the first two Greek letters of the word "Christ" (Greek: ΧΡΙΣΤΟΣ, or Χριστός) — Chi (χ) and Rho (ρ). It was first used by the Roman emperor Constantine I. Since the vexillum consisted of a flag suspended from the crossbar of a cross, it was ideally suited to symbolize crucifixion. The Chi-Rho symbol was also used by Greek scribes to mark, in the margin, a particularly valuable or relevant passage; the combined letters Chi and Rho standing for chrēston, meaning "good."